
How to Arc Weld is all about learning the basics of one of the most popular welding methods used in construction, repair, and fabrication.
Arc welding uses electricity to create intense heat, melting metal and joining it together. It’s a versatile and cost-effective technique, making it essential for beginners and experienced welders alike.
Whether you’re new to welding or looking to improve your skills, understanding the process, tools, and techniques of arc welding is key to creating strong, reliable welds.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to arc weld step-by-step to help you get started!
What is Arc Welding?

Arc welding is a type of welding that uses electricity to create a high-temperature arc to melt metal and join two pieces of metal together. It is a versatile and widely used welding process that can be used to weld a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
Arc Welding Process
The process of arc welding involves creating an electric arc between an electrode and the metal being welded. The arc generates intense heat, which melts the metal and forms a weld pool. As the weld pool cools, the metal solidifies and forms a strong bond between the two pieces of metal.
Arc welding differs from other types of welding in that it uses an electric arc to generate heat, whereas other types of welding, such as gas welding, use a flame to generate heat.
Additionally, arc welding can be performed using a variety of welding techniques, including stick welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding.
Arc Welding Advantages
One of the advantages of arc welding is its versatility. It can be used to weld a variety of metals and can be performed in a variety of settings, including in the field or in a workshop.
Additionally, arc welding is a relatively simple process that can be learned quickly with the right training and equipment.
Safety Precautions for Arc Welding

When it comes to arc welding, safety should always be your top priority. Before you begin welding, make sure you have taken the necessary safety precautions to protect yourself and those around you.
Here are some essential safety measures to take before beginning to arc weld:
1. Personal Protective Equipment
Welding produces intense heat and bright light, which can cause serious injuries if proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is not worn. Here are some PPE you should consider:
- Welding helmet with a cover plate
- Safety glasses or goggles
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Welding gloves
- Leather boots
- Earplugs or earmuffs
- Respirator for protection from toxic fumes
2. Workspace Setup
Your workspace should be set up in a way that minimizes the risk of accidents. Here are some workspace safety precautions:
- Keep your workspace clean and free of clutter
- Remove all flammable materials from the area
- Make sure your welding machine is in good condition and properly grounded
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby
- Ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes and gases
4 Basic Equipment Needed for Arc Welding
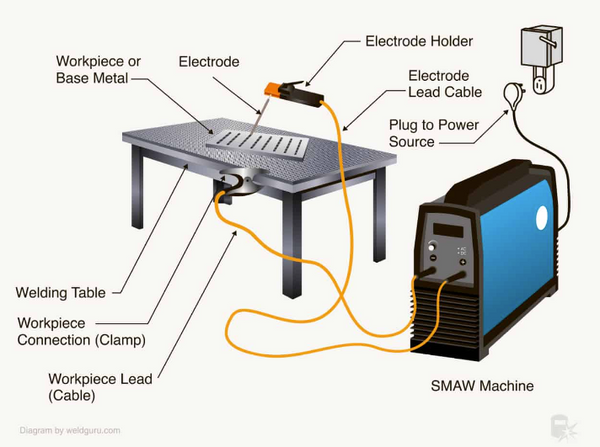
Arc welding is a process that requires specific equipment to create a strong and reliable weld.
Here is a list of the essential equipment you need to get started with arc welding:
1. Welding Machine
The welding machine is the most critical piece of equipment for arc welding. It provides the electrical current necessary to create an arc between the electrode and the metal being welded.
There are different types of welding machines available, such as AC, DC, and AC/DC. The type of welding machine you choose will depend on the type of metal you are welding and the thickness of the material.
2. Electrodes
Electrodes are the filler material used to create the weld. They are made of different materials, such as steel, aluminum, and nickel alloys. The type of electrode you choose will depend on the type of metal you are welding and the welding technique you are using. Electrodes come in various sizes and shapes, and you must choose the right one for the job.
Learn more about Different Type of Welding Rods in this detailed guide.
3. Clamps
Clamps are used to hold the metal being welded in place. They come in different sizes and shapes and are designed to hold the metal securely to prevent movement during the welding process. Clamps are essential for creating a clean and precise weld.
4. Protective Gear
Protective gear is crucial for arc welding. The intense heat and bright light produced during the welding process can cause severe burns and eye damage. Therefore, it is essential to wear protective gear such as welding helmets, gloves, and safety glasses.
Welding helmets protect your face and eyes from the bright light produced during the welding process. Welding gloves protect your hands from burns, while safety glasses protect your eyes from flying debris and sparks.
Preparing to Arc Weld
Before you start arc welding, it is essential to prepare both the material and equipment to ensure a successful welding process.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in preparing for arc welding is to clean the metal surface to remove any dirt, grease, or rust. This can be done using a wire brush or grinder. Cleaning the metal ensures that the welding process is not impeded by any contaminants that may weaken the weld.
If the metal consists of two pieces that are to be joined in the welding process, you may need to prep, or weld prep them, by grinding a beveled edge on the sides that are to be joined. This allows for sufficient penetration of the weld arc to melt both sides to a molten state so the filler metal bonds through the sectional thickness of the metal.
2. Equipment Preparation
Once the material is prepared, it's time to set up the welding machine. First, plug in your welder and switch it on. You should hear a humming sound coming from your transformer.
Next, ensure that you have the correct electrode for the metal you are welding. The electrode is the metal wire that conducts the electric current used to create the arc.
Hold the electrode gun with your dominant hand, making sure that the angle of the rod is such that you can easily strike an arc. Double-check that you have the amperage set to between 80 and 100 amps on the welding machine.
Finally, ensure that you have the necessary safety equipment, including welding gloves, a welding helmet, and protective clothing.
How to Arc Weld: Step-by-Step Guide
Arc welding is a process that requires precision and attention to detail. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
-
Prepare your work area: Before you start welding, make sure your work area is clean and free of any flammable materials. You should also wear protective clothing, including a welding helmet, gloves, and appropriate clothing.
-
Set up your equipment: Ensure that your welding machine is set up correctly and that you have the right electrode for the job. Check that your electrode is clean, dry, and free of any defects.
-
Strike the arc: To start welding, you need to strike the arc. You can do this by tapping the end of the electrode on the base metal or by dragging it along the surface like striking a match. Once you have struck the metal, immediately lift the rod away by about a quarter to half an inch, which produces the arc.
-
Lay the bead: Once the arc is established, move the electrode towards the joint you want to weld. Keep the electrode at a consistent distance from the base metal, and move it in a circular or side-to-side motion to create a bead.
-
Control the heat: As you weld, you need to control the heat to avoid overheating the metal and causing it to warp or deform. You can do this by adjusting the amperage on your welding machine or by moving the electrode further away from the metal.
-
Finish the weld: Once you have completed the weld, let it cool before removing any clamps or fixtures. Use a wire brush to remove any slag or debris from the weld, and inspect it for any defects.
Common Arc Welding Techniques
There are several common arc welding techniques that you can use depending on the type of weld you need to make and the materials you are working with. Here are some of the most popular techniques:
1. Whip and Pause Technique
The whip and pause technique is a popular technique used for welding thin metals. This technique involves moving the electrode in a whipping motion while pausing at the end of each whip. The whip and pause technique is ideal for creating a strong weld without burning through the metal.
2. Circle Technique
The circle technique is a common technique used for welding thicker metals. This technique involves moving the electrode in a circular motion around the weld joint. The circle technique is ideal for creating a wider weld bead and for welding thicker materials.
3. Weaving Technique
The weaving technique is a popular technique used for welding wider joints. This technique involves moving the electrode in a weaving motion while maintaining a consistent arc length. The weaving technique is ideal for creating a wider weld bead and for welding wider joints.
4. Tack Welding
Tack welding is a technique used to hold two pieces of metal together temporarily before making a final weld. This technique involves making small welds at various points along the joint to hold the pieces of metal in place.
5. Spot Welding
Spot welding is a technique used to join two pieces of metal together at specific points. This technique involves applying a high amount of heat to a specific point on the metal until it melts and fuses with the other piece of metal.
Common Arc Welding Problems and How to Solve Them
As an arc welder, you may encounter a few common problems while welding. Here are some of the most common issues and their solutions:
1. Electrode Sticking
One of the most common issues welders face is electrode sticking. This happens when the electrode gets stuck to the workpiece, making it difficult to remove.
To Electrode Sticking, make sure you're using the correct electrode for the job. Also, keep the electrode dry and clean before use. If the electrode gets stuck, try tapping it lightly with a hammer to loosen it.
You can also use pliers to remove it, but be careful not to damage the electrode or the workpiece.
3. Spatter
Spatter is another common issue that occurs during arc welding. It happens when small droplets of molten metal are scattered around the weld area.
To avoid spatter, make sure you're using the correct welding technique. Also, keep the welding area clean and free of any debris.
If spatter occurs, use a wire brush to remove it. You can also adjust the welding parameters to reduce spatter.
4. Weld Cracks
Weld cracks can occur due to a variety of reasons, including incorrect welding technique, improper preparation of the workpiece, or using the wrong welding parameters.
To avoid weld cracks, make sure you're using the correct welding technique for the job. Also, properly prepare the workpiece by cleaning it thoroughly and ensuring that it's free of any defects.
Finally, adjust the welding parameters to ensure that you're using the correct settings for the job.
Conclusion
Learning how to arc weld is a valuable skill that opens up opportunities for DIY projects, repairs, and professional work.
By following the step-by-step guide, beginners can understand the basics of setting up equipment, preparing materials, and creating strong welds.
Practice is key, so start with simple projects to build your confidence and improve your technique. Remember to always wear the right safety gear and follow safety guidelines. Arc welding may seem challenging at first, but with patience and the right tools, anyone can master it. Now, get out there and start practicing your welding skills!
Ready to take the next step? Purchase your Arc Welder from ArcCaptain today and enjoy top-quality performance. If you need more assistance, please don't hesitate to contact us!
Frequently Asked Questions on How to Arc Weld
How to do arc welding for beginners?
If you are new to welding, arc welding is a great starting point. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), also known as stick welding, is considered good for beginners. It requires less equipment and is more forgiving with regards to weld cleanliness. Its simplicity makes it a great starting point for those new to welding. Before you begin, make sure you have the right equipment, including a welding machine, electrode holder, ground clamp, and welding helmet.
How do you start an arc when stick welding?
Starting an arc when stick welding can be tricky, but it is essential to get a good weld. Follow these steps to start an arc:
- Clean the metal surface to be welded.
- Set your electrode to the correct amperage for the thickness of the metal you are welding.
- Hold the electrode holder at a 90-degree angle to the metal surface.
- Strike the electrode against the metal surface with a quick motion, then pull it back about 1/8 inch to establish an arc.
- Once the arc is established, you can begin welding.
What is the best arc welding method?
The best arc welding method depends on the project you are working on. There are several distinct methods, each tailored to specific applications and materials. Understanding these different arc welding techniques is essential for choosing the right approach to match your welding project's requirements. The primary types of arc welding are:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
What is the strongest arc weld?
The strength of an arc weld depends on several factors, including the type of metal being welded, the welding method used, and the skill of the welder. However, in general, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) produces the strongest arc welds. GTAW, also known as TIG welding, uses a tungsten electrode to create an arc that melts the metal being welded. This creates a strong, precise weld that is ideal for critical applications such as aerospace and medical equipment.
